Hello @swolny
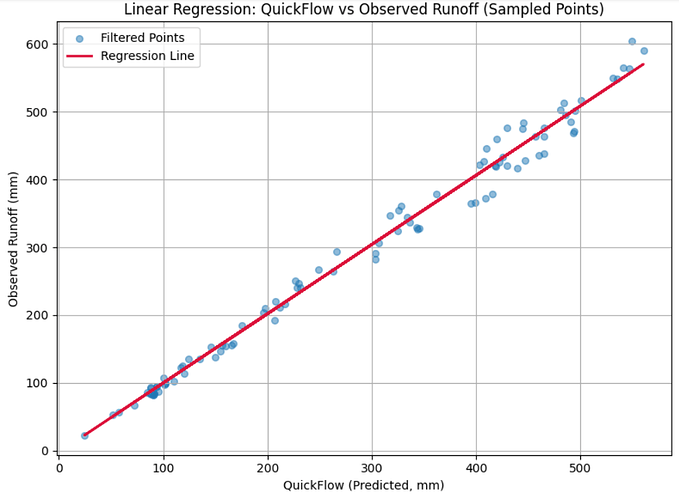
I am writing to share the results of the validation performed on our machine learning-based precipitation estimation using the WorldClim dataset for the year 2022. To ensure model reliability, a tolerance level was applied to address potential issues of overfitting and underfitting during training.
The validation results are as follows:
- Root Mean Square Error (RMSE): 18.02 mm
- Percentage RMSE Error: 6.26%
- R² Score: 0.9878
These results indicate a high level of model accuracy and robustness. The validation plot for 2022 is attached for your reference.
Please let me know if further details or clarification are required.
CODE FOR VALIDATION
import rasterio
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
import xarray as xr
from rasterio.warp import reproject, Resampling
from rasterio.transform import from_bounds
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=FutureWarning)
# === Step 1: File Paths ===
qf_path = "/content/QF.tif"
terra_path = "/content/TerraClimate_q_2022.nc"
# === Step 2: Load QuickFlow TIFF ===
with rasterio.open(qf_path) as src_qf:
qf = src_qf.read(1)
qf_meta = src_qf.meta.copy()
qf = np.where(qf == src_qf.nodata, np.nan, qf)
# === Step 3: Load TerraClimate runoff and compute annual runoff ===
ds = xr.open_dataset(terra_path)
obs_data = ds['q'].sum(dim='time') # Annual runoff
obs_vals = obs_data.values
# === Step 4: Build Transform for Observed Data ===
lat = ds['lat'].values
lon = ds['lon'].values
height, width = len(lat), len(lon)
transform_obs = from_bounds(lon.min(), lat.min(), lon.max(), lat.max(), width, height)
# === Step 5: Reproject TerraClimate to Match QF ===
obs_resampled = np.empty_like(qf)
reproject(
source=obs_vals,
destination=obs_resampled,
src_transform=transform_obs,
src_crs="EPSG:4326",
dst_transform=qf_meta['transform'],
dst_crs=qf_meta['crs'],
resampling=Resampling.bilinear
)
obs_resampled = np.where(obs_resampled == 0, np.nan, obs_resampled)
# === Step 6: Flatten and Clean ===
qf_flat = qf.flatten()
obs_flat = obs_resampled.flatten()
mask = (~np.isnan(qf_flat)) & (~np.isnan(obs_flat))
qf_clean = qf_flat[mask]
obs_clean = obs_flat[mask]
# === ✅ Step 7: Apply Relative Error Tolerance (10% of individual observed values) ===
rel_tol = 0.10 # 10% relative tolerance
mask_tol = (np.abs(qf_clean - obs_clean) <= rel_tol * obs_clean)
X = qf_clean[mask_tol].reshape(-1, 1)
y = obs_clean[mask_tol]
if len(X) == 0:
raise ValueError("No points passed the relative error tolerance filter.")
# === Step 8: Train Linear Regression ===
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X, y)
y_pred = model.predict(X)
# === Step 9: Evaluation ===
rmse = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y, y_pred))
r2 = r2_score(y, y_pred)
mean_obs = y.mean()
rmse_percent = (rmse / mean_obs) * 100
# === Step 10: Print Results ===
print(f"Tolerance applied: ±10% of each observed value")
print(f"Points used in regression: {len(X)} / {len(qf_clean)} ({(len(X)/len(qf_clean))*100:.2f}%)")
print(f"Mean of Observed Runoff = {mean_obs:.2f} mm")
print(f"RMSE = {rmse:.2f} mm")
print(f"Percentage RMSE Error = {rmse_percent:.2f}%")
print(f"R² Score = {r2:.4f}")
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# === Limit to 100 random samples for visualization ===
np.random.seed(42) # For reproducibility
if len(X) > 100:
indices = np.random.choice(len(X), 100, replace=False)
X_vis = X[indices]
y_vis = y[indices]
y_pred_vis = y_pred[indices]
else:
X_vis = X
y_vis = y
y_pred_vis = y_pred
# === Plot ===
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
plt.scatter(X_vis, y_vis, alpha=0.5, s=30, label='Filtered Points')
plt.plot(X_vis, y_pred_vis, color='crimson', linewidth=2, label='Regression Line')
plt.xlabel("QuickFlow (Predicted, mm)")
plt.ylabel("Observed Runoff (mm)")
plt.title("Linear Regression: QuickFlow vs Observed Runoff (Sampled Points)")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
![]() One of the key objectives of my study is:
One of the key objectives of my study is:![]() Current input factors used:
Current input factors used: